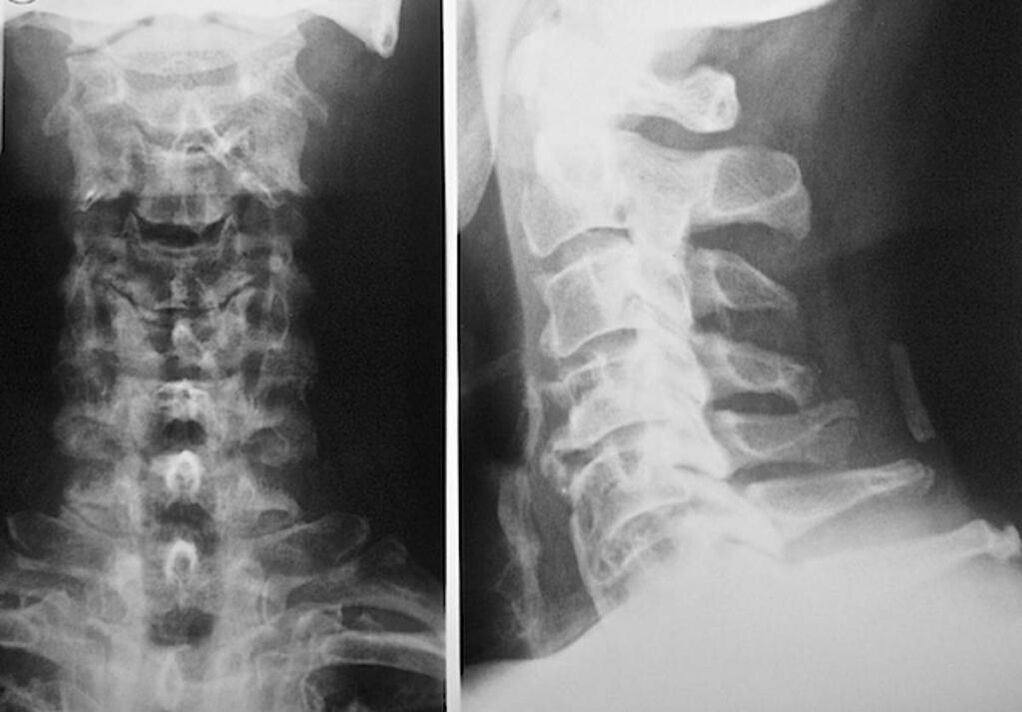
Osteochondrosis - degenerative changes in articular cartilage with partial destruction of the intervertebral disc between the vertebrae. Cervical osteochondrosis is characterized by slow destruction of the tissue between the vertebrae that support the head and develops over the years. If in the last century, the disease was primarily diagnosed in people 30 and older, today's orthopedic surgeons make such a diagnosis even in schoolchildren. The treatment time for cervical osteochondrosis is very long. Maintenance therapy should be administered even during remission.
early symptoms of disease
The cervical spine is smaller in size than the thoracic and lumbar spine. But they carry a heavy load: a person's neck performs many complex movements every day. Office workers who are forced to sit in the same position in front of a computer for hours on end often develop cervical osteochondrosis. In this case, treatment includes not only eliminating the pain, but also forcing lifestyle changes. Sitting in front of a monitor for long periods of time can be a big test for your spine.
The following causes of cervical osteochondrosis can be distinguished:
- hereditary;
- a sedentary lifestyle;
- extreme physical activity;
- neck injury;
- cervical spine abnormalities;
- Constantly incorrect body position during sleep.
Orthopedics and neurology distinguish four stages of the disease. In the first two, the disease does not cause severe pain, but it cannot be ignored either.
In the first stage, the disease manifests as frequent headaches and a slight pulling sensation in the neck. Almost all patients do not take this mild symptom seriously. Headaches are attributed to fatigue or lack of sleep. Most patients prefer to simply take pain relievers.
Over time (sometimes this process can last for years), the disease inevitably enters a second stage. The danger of osteochondrosis is the frequent occurrence of so-called radiculopathy. Mostly, it manifests itself in the second stage and further aggravates as the osteochondrosis progresses. Root syndrome is compression of nerve endings in the cervical spine. After that, headaches were added to many other conditions. This is vision and hearing loss, vestibular organ dysfunction, excruciating migraines with or without aura, numbness in the hands.
Often, patients don't see a doctor until they develop radiculopathy. Most importantly, they only care about its symptoms. Treatment and necessary rehabilitation for cervical osteochondrosis will not counteract all the consequences of radiculopathy. You can only temporarily stop the progression of the disease and prevent larger complications.

later disease manifestations
There are also third and fourth stages of the disease, which are simply impossible to ignore. Even patients who are surprisingly disregard for their own health sound the alarm and go to the doctor.
Stage III cervical osteochondrosis, if not accompanied by radiculopathy, can cause frequent severe headaches in patients. Characterized by pain directly in the neck and shoulders. The patient was forced to continue to use ointments with warming and analgesic properties. Massage is helpful in the third stage. It's important to understand that getting rid of the disease completely won't work. Only long-term remission can be achieved -- that's the goal of treatment.
Symptoms of stage IV cervical osteochondrosis: The spine is clearly deviated by visual inspection and there is severe pain in the area. If there is also radiculopathy, the patient often experiences very severe dizziness and may pass out after he makes one or the other strenuous physical movement. Depending on where and how severely the nerve endings are pinched, vision or hearing may deteriorate significantly.
In later stages, irritated reflex syndrome may also occur, in which there is often severe throbbing pain in the back of the head, and pain descending to the thoracic spine. They can reach such intensity that the patient cannot fall asleep or perform usual physical movements. Such symptoms may also occur with strong displacement of the vertebrae. Ninety percent of advanced cervical osteochondrosis is associated with irritable reflexes or radiculopathy.
In some cases, the disease is complicated by two of these pathologies at the same time. In this case, the treatment of cervical osteochondrosis with folk remedies will not work. An integrative approach is important, which involves the use of professional methods (injection, massage, physiotherapy, taking pain relievers) and general methods (swimming, exercise therapy, lifestyle).

Symptoms depend on damaged nerve roots
Osteochondrosis of the 1st cervical vertebra is accompanied by numbness in the occipital region in the early stages of disease development. In the later stage - severe pain in the area. The best treatment is to use warm and numbing creams and massage. Once every six months, it is necessary to inject B vitamin preparations.
Osteochondrosis of the 4th and 5th cervical vertebrae is accompanied by invasion of extremity sensitivity and the presence of pain in the forearm, chest area. Treatment - Massage the neck area and numb areas of the body. Shows continued regular use of B vitamins (at least every six months, preferably quarterly). Physical therapy is also effective.
Osteochondrosis of the 6th cervical vertebra with shoulder and neck pain. Frequent headaches. Vision may begin to deteriorate - myopia and astigmatism develop. The principles of treatment are the same as when other vertebrae are involved. Only the accompanying symptoms - vision and hearing loss - you also need to be aware of. Regular visual hygiene, eye exercises, special drops that relax the optic nerve.
Osteochondrosis of the 7th cervical vertebra with damage to nerve endings in the region of the 5th, 6th, and 7th vertebrae. It occurs in men and women of any age. This is the most common cervical osteochondrosis. Symptoms of compression of the C6 and C7 nerve endings are periodic numbness of the fingers and hands, pain in the neck, forearms and lower-scapulae, back and up to the lumbar spine.
Osteochondrosis Diagnosis: Which Doctor to Contact
To diagnose and prescribe treatment for cervical osteochondrosis, you should sign up for consultation with a neuropathologist and an orthopedic surgeon. A neurologist can prescribe remedies for disease manifestations that affect the state of nerve endings. This makes sense if the disease is accompanied by radicular syndrome. An orthopaedic surgeon will assess the condition of the spine and diagnose the presence of other conditions: scoliosis, lordosis, etc.
To diagnose and accurately assess the condition of the intervertebral disc, the following research methods are used:
- radiography.
- CT scan.
- Magnetic tomography.
- Ultrasound scan of blood vessels in the neck.
Each of them is completely safe for health and poses no threat of overexposure. The diagnosis of cervical osteochondrosis, the treatment of which will occur for the rest of your life, can be made after a simple visual examination. Any orthopedic surgeon can easily do this. An exception is the first stage of the disease, when no visible lesions in the cervical region are found.
traditional medicine treatments
How to treat cervical osteochondrosis? Whichever method you choose, it should be remembered that in order to achieve relief, you must regularly monitor the condition of your neck. Osteochondrosis cannot be completely cured. After a while, these symptoms will surely make themselves felt again, and their intensity will directly depend on the patient's attitude toward their own health.
Below is a list of the most effective measures to eliminate osteochondrosis symptoms:
- physiotherapy;
- neck massage;
- take pain relievers;
- A course of B vitamins;
- physiotherapy;
- swimming.
The patient must remember that he should not engage in athletics (running, jumping, plyometrics), strength training. This will inevitably lead to the deterioration of the condition. You can't sit in one position for a long time. Even if your office work involves long hours at the monitor, you need to get up every hour to warm up your collar area for ten minutes and do some light stretches.
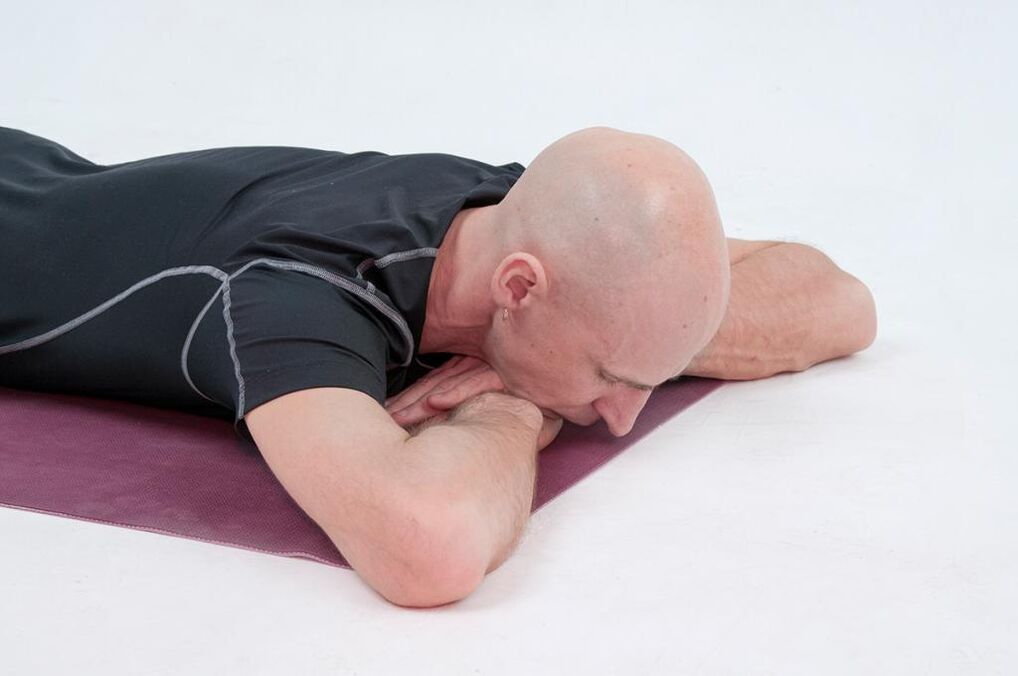

Comprehensive physiotherapy exercises for cervical osteochondrosis
Cervical osteochondrosis can be treated at home with the help of special exercises. They have to be performed every day or you won't get noticeable results.
- Stand up straight and that's it. Raise your hands, take a deep breath, stand on tiptoe, and stretch as far as you can. Perform several repetitions.
- Starting Position - Stand on your feet with your back straight and your arms lowered freely along your body. The left ear touches the left shoulder and the right ear touches the right shoulder. Do ten repetitions in each direction at a slow pace without sudden movements.
- The starting position is the same as in the previous exercise. Touch your chin to your sternum, then gently tilt your head back. Exercise should be abandoned if it is accompanied by pain or discomfort.
- Sit on a chair or hard floor with your back straight. You can cross your legs in lotus position. Perform a circular rotation of the head - first clockwise, then counterclockwise.
- Lie down on the hard floor. Arms and legs stretched. Practice the "boat": tear off the surface of the head, arms, and legs and lift them as high as possible. Hold this pose for as long as possible. This exercise is useful not only for the cervical spine, but also for the thoracic and lumbar spine.
Physical therapy exercises should be done cautiously and slowly. Sudden movements can make the pain worse.
If the workout can be followed by a therapeutic warm massage on the neck collar area - great. This way of combining two treatments at the same time is very good.
Blocking Cervical Osteochondrosis Pain Syndrome
The main drugs used to treat cervical osteochondropathy with vertebral displacement are non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). In addition, for cervical osteochondrosis, topical NSAID gels and ointments are preferred.
In this regard, ointments and creams containing snake venom and bee venom in the composition are effective. Among topical means, topical irritants and chondroprotective agents are shown.
If the pain is too severe, a one-time, strong pain reliever can be used. Sometimes colds can make osteochondrosis worse. In this case, in order to eliminate all symptoms of acute respiratory viral infections and rickets, a drug based on the active ingredient paracetamol will help.
Application of B vitamins in traditional therapy of diseases
Why do neuropathologists always prescribe B vitamins as part of comprehensive treatment for cervical osteochondrosis? The explanation is simple. With radiculopathy, nerve endings are affected, and vitamins are the easiest way to support their function. The most effective form of application is intramuscular injection. When taken orally, B vitamins are only partially absorbed. When injected intramuscularly, they enter the bloodstream almost immediately.
Treating cervical osteochondrosis at home
For complex treatments, there is no need to go to the hospital at all. It is entirely possible to achieve relief at home. It would be great if patients could inject independently. Then you can't be in the clinic every day.
Methods of treating cervical osteochondrosis with folk remedies:
- Bathing with salt and soda can reduce pain and relax your body. This is especially good at bedtime. You should take a bath in moderately warm water, then dissolve a kilogram of salt and about 500 grams of soda in it.
- Paraffin application is excellent. Melt paraffin or wax, cool to a comfortable temperature, and apply to damaged areas. Such compaction can be done 2 times per week.
- To reduce the inflammatory process, you can take herbal soups. You need to mix 1 tablespoon. l. Flowers of St. John's wort, chamomile, marigold, and yarrow. Add 1 tablespoon to them. l. Thyme and dandelion leaves. Now you should take 2 tablespoons. l. Pour the resulting mixture into a liter of boiling water and stick to it. Taking a decoction of 1/4 glass 3 times a day for 3 weeks is enough.
- If you do not believe in pharmaceutical preparations, you can prepare an ointment for cervical osteochondrosis. You will have to take equal parts coriander fruit, birch buds, dandelion root, and mint grass. Grind three tablespoons of the mixture to a powder, pour in 1/2 cup of boiling water, and simmer for 5 minutes. To the resulting mass were added 75 grams of vegetable oil and pork fat. Cool and rub into affected area 4 times a day. Store the ointment in the refrigerator.
- Great for osteochondrosis and compression. For example, from honey and potatoes. Grate a large tuber on a fine grater and mix with honey in a 1: 1 ratio. The resulting mixture was applied to the affected area for 45 minutes.
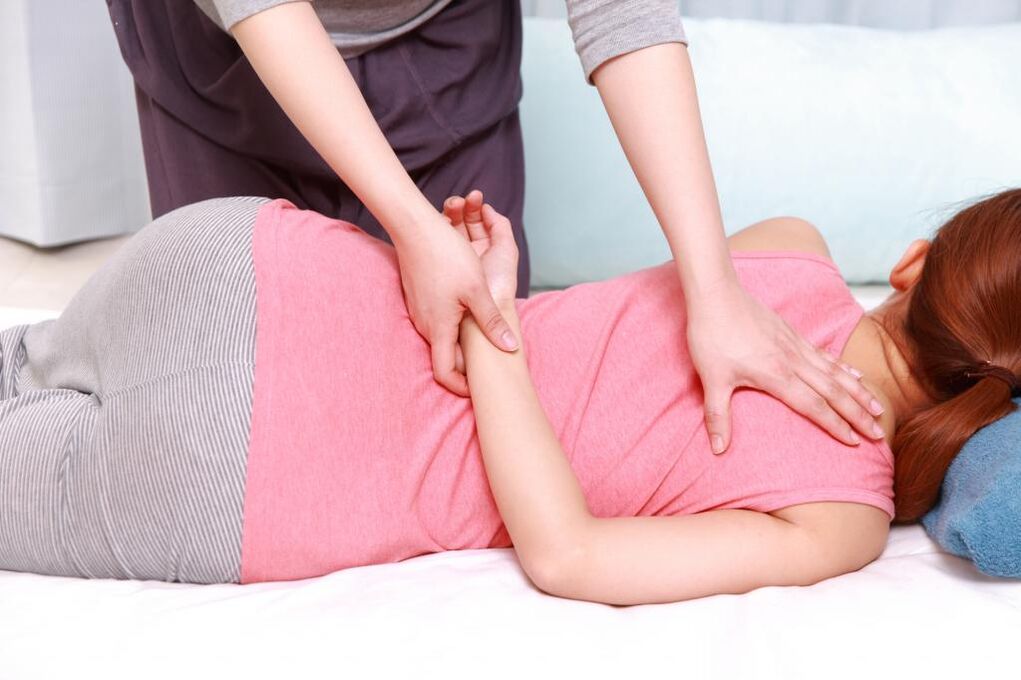
For cervical osteochondrosis, massage is the first therapy to relieve tension and pain. In order to give yourself massage therapy, you need good flexibility. Older people often cannot even raise their arms to the required height. But they found a way out: They asked a young relative for a massage.

Patient feedback on treatment outcomes
According to numerous reviews of orthopaedic and neurological patients, the best treatment is to use all procedures in combination. Treating cervical osteochondrosis using only folk remedies is futile.
Some patients have noticed that a series of procedures with a good massage therapist has actually brought them back to life and their ability to work has increased.
Some patients respond positively to physical therapy exercises only. They started exercising at home regularly, purchasing a subscription to therapeutic swimming lessons in the pool. Regular exercise with yoga and spine stretching helps some people. The feeling after this pose: body light, no pain, less stress.
If you regularly load your body with this activity, you can go into a long period of remission and forget about the symptoms of cervical osteochondrosis.