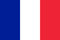
Typical symptoms of spinal pain
Osteochondrosis of the lumbosacral vertebrae causes progressive destruction of the intervertebral discs and is therefore very symptomatic. The most common manifestations include:- Severe pain concentrated in the lower back.
- Feeling of fullness and stiffness.
- The pain can be severe or occur along the entire length of the lower limb.
- Feeling numb in back and legs.
- Urinary incontinence.
- Frequent urge to empty your bladder.
- Exacerbation of genitourinary diseases.
Main features of osteochondrosis pathology
- This type of pathology is the most common of all types of osteochondrosis. Confirmed cases account for approximately 65% of the total recorded cases.
- There is a clear link between this disease and natural age-related changes. Statistics show that 70 years later, almost 80% of people suffer from manifestations of this disease.
- The disease can appear at a younger age. At-risk groups include people who engage in strenuous physical labor or remain in monotonous postures for long periods of time.
- The cause of osteochondrosis may be congenital abnormalities or various predisposing factors.
Causes of spinal disease

- overweight. People who are overweight are at risk because the extra weight puts more pressure on the spine.
- Back injuries and injuries.
- Passive lifestyle. There are even some professions whose representatives are more susceptible to the disease - these include drivers, office workers and other types of work characterized by long-term exposure to the same positions.
- Lift heavy objects and loads. There are certain rules, and if they are not followed, this disease can occur.
- The back is often stressed. They are related not only to a person's professional activities, but also to sports.
- Eat the wrong foods. The disease will progress if the diet is deficient in nutrients important for normal metabolic processes and improved bone structure. This is why diet is one of the methods of complex therapy.
- genetic factors.
- Hypothermia of the body.
- A person's level of physical activity is low.
- Flat feet and scoliosis.
Sacrolumbar osteochondrosis
Main stages of disease:
- The first stage. In the early stages, pain occurs, which occurs under the influence of various loads. This condition is characterized by low back and lower back pain - these are certain types of pain that can be stable or severe.
- second stage. The stability of the intervertebral discs is violated, causing muscle spasms. The annulus fibrosus structure is destroyed and the gelatinous contents protrude. The pain syndrome becomes more persistent and pronounced.
- The third phase. A prolapsed disc causes nerve compression. This condition causes severe pain in the back and legs, impaired sensitivity, pelvic organ dysfunction, and muscle atrophy.
- The fourth stage. At this stage, bone growth in the lesion and changes in spinal structure can be diagnosed. It becomes more difficult for the patient to move and the pain becomes constant and unbearable, which may lead to total disability in the future.
Diagnostic methods for back problems
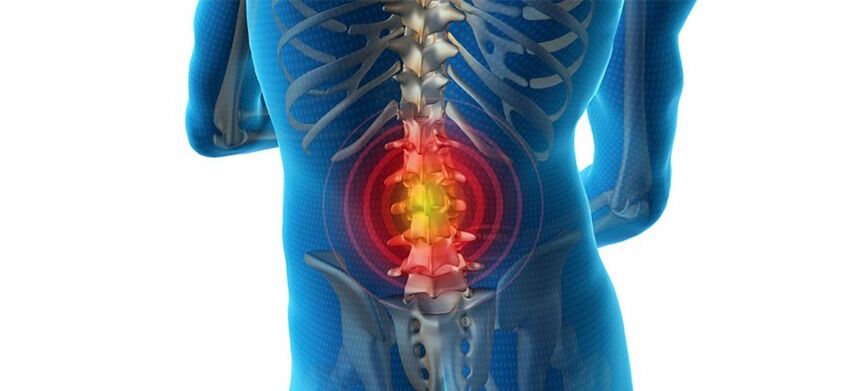
- X-ray examination. With its help, you can evaluate whether there are any abnormalities in the condition of the vertebrae. You can see a decrease in disc height, the formation of osteophytes, and a narrowing of the joint space.
- CT scan. It allows you to see the structural condition of the entire spine and its individual components. Allows you to determine the stage of the disease and whether pathology is present in the bone structure.
- MRI. This method is the most informative of all the methods mentioned above. With it you can see intervertebral hernias, identify nerve root compression and other pathologies. CT is used if the patient contraindicates this diagnostic method.
Main methods of treating lumbosacral spine
- Chondroprotectant. They have a positive effect on cartilage tissue and promote regeneration processes.
- Muscle relaxants. Their purpose is to eliminate muscle spasms.
- external means. Creams, gels, and ointments are designed to eliminate severe symptoms of the disease, but are not as effective as injections and oral medications.
physiotherapy
- Ultra high frequency therapy.Exposure to high frequency electromagnetic fields. It has anti-inflammatory, analgesic properties and also promotes the initiation of regenerative processes.
- Amplify the pulse.Low-frequency current is applied to problem areas of the body. It has the effect of dilating blood vessels, relieving pain and spasm.
- electrophoresis and electrophoresis.Uses ultrasound and direct current to introduce drugs into deep tissues.
Diet-Comprehensive Treatment of Osteochondrosis
- Citrus fruits (in the absence of allergies).
- olive oil.
- Fresh herbs and vegetables.
- mineral water.
- Fish and foods containing high amounts of phosphorus, protein, magnesium and calcium.
- Dairy products and fermented dairy products.
How to prevent low back pain
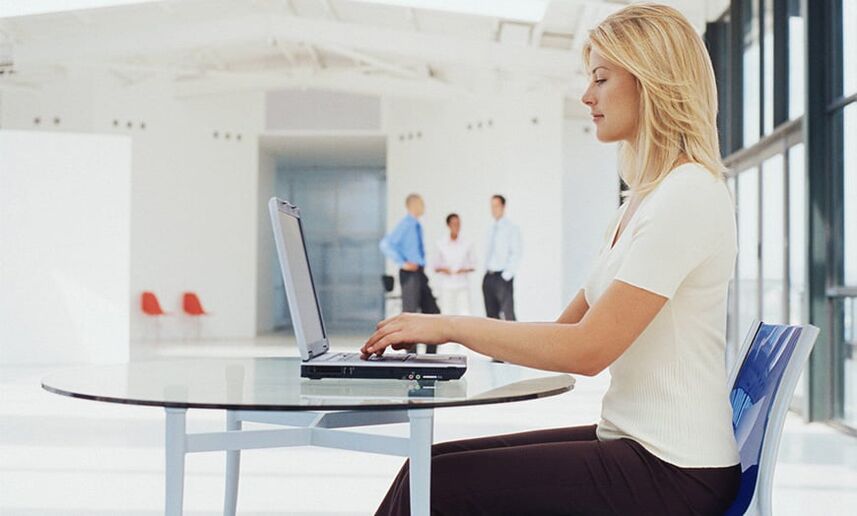

- Proper organization of the workplace.Monitor your body posture and try to avoid awkward postures. If you spend a lot of time in front of the computer, invest in a comfortable chair with a backrest that supports your spine.
- Take a break from work.Warm up by standing up from your seat frequently and turning your body regularly. Squats and curls are also useful.
- Normalize your day.First, we’re talking about rest, so try to go to bed early and rule out sitting in front of the computer for long periods of time. It is important to choose the right orthopedic mattress that will support your spine while you sleep.
- Get rid of bad habits.
- Avoid strenuous exercise and heavy lifting.Swimming, yoga and regular walks in the fresh air are a great option.